Benzotriazole is a diverse chemical that is critical in the prevention of corrosion in a wide range of applications. Due to its effectiveness at lower concentration, Benzotriazole is an ideal solution for copper corrosion prevention needs for environments such as waste water treatment and management.
Common Applications for Benzotriazole
Benzotriazole is most commonly used as a corrosion inhibitor for copper and its alloys. Applications include:
- Industrial Water Treatment
- Automotive Fluids
- Metalworking Fluids
- Lubricants
- Heat Transfer Fluids
- Detergents and Cleaning Agents
Additionally, Benzotriazole is also used as a chemical intermediate to produce UV stabilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other derivatives.
Benzotriazole Synthesis
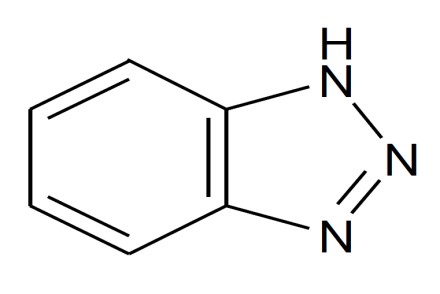
Benzotriazole is synthesized by diazotization of ortho-phenylenediamine with nitrous acid. Commercial production typically requires high pressure reaction followed by additional processing and purification.
Advantages of Benzotriazole in Corrosive Environments
- Benzotriazole is highly effective at very low concentrations with recommended dosage in the part-per-million range.
- Benzotriazole reacts with copper containing metals to form a long-lasting insoluble film that prevents oxidation of the metal surface.
- Benzotriazole reacts with soluble copper ions, to prevent galvanic corrosion and copper induced pitting of dissimilar metals.
Common Forms of Benzotriazole
The most common form of benzotriazole is a solid flake, with other forms including granular, fine powder, and crystalline needles. Many users prefer liquid forms for safety and ease of handling, such as sodium benzotriazole in water, or benzotriazole dissolved in glycols, alcohols, or esters.
Physical Characteristics
Benzotriazole is a white to light yellow solid with a chemical formula of C6H5N3.
- Molecular Weight: 119.13 g/mol
- Density: 1.36 g/cm3 at 20°C
- Melting Point: 98.5°C
- Boiling Point: 204°C
- Solubility Limit in Water: 2% or 20 g/L
- pH: Benzotriazole is a weak acid with a pKa of 8.2
Shelf Life and Stability
Benzotriazole has a shelf-life of five years or longer if stored correctly. Benzotriazole should be stored in sealed containers, in a cool, dry, ventilated area away from any heat source. Temperature, moisture, and other adverse conditions can shorten the life of the material.
Environment and Safety of Benzotriazole
Studies have shown mixed results on biodegradation of benzotriazole, with some showing effective degradation by microorganisms, while other studies show resistance to biodegradation under varying conditions. Benzotriazole has been shown to degrade slowly by UV irradiation, however it is assumed to be persistent in the environment. Benzotriazole should be used and disposed of in accordance with all federal, state, and local regulations.
Benzotriazole is considered hazardous by ingestion and causes serious eye irritation. In addition, benzotriazole is harmful to aquatic organisms.






